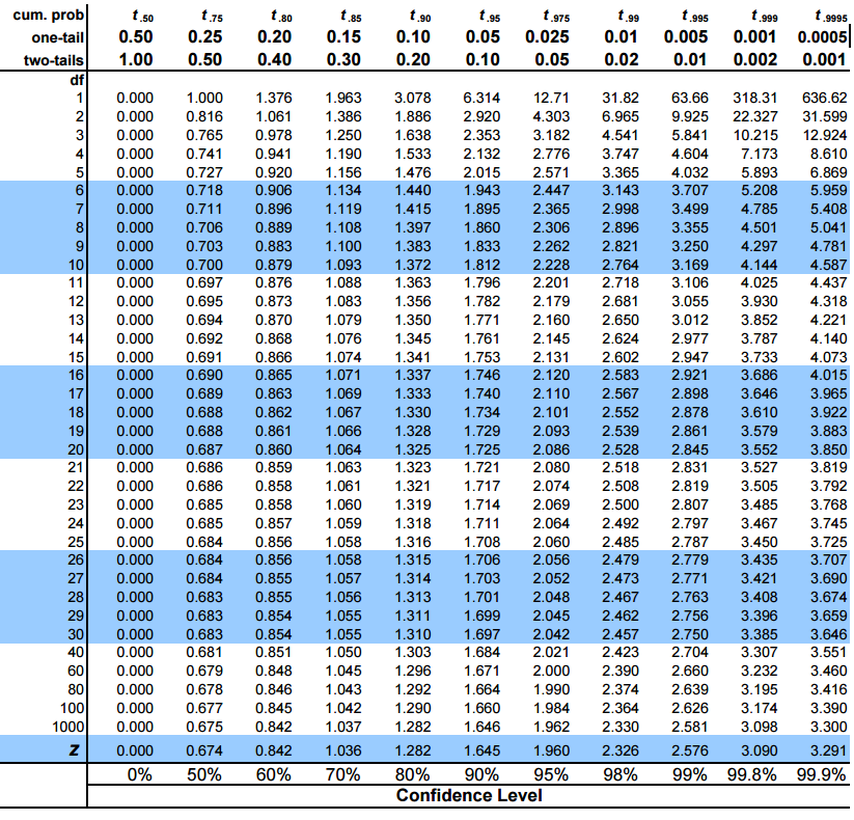
T Distribution Table – A t table, also known as the Student’s t table, is a statistical table showing the t distribution’s critical values. The t-distribution is a probability distribution used in many statistical tests, such as the t-test for independent and the t-test for paired samples.
The t table is used to find the critical value of t for a given significance level and degrees of freedom. The effectiveness level is the possibility of denying the null view when it is true. The degrees of freedom are the number of independent observations in the sample.
T Distribution Table
To use the t table, find the significance level in the table. Then, find the degrees of freedom in the table. The intersection of these two values is the critical value of t.
For example, if the significance level is 0.05 and the degrees of freedom are 10, the critical value of t is 1.812. This means that if the t statistic for a t-test is more significant than 1.812, we can deny the null hypothesis at the 0.05 importance level.
The t table can be found in most statistics textbooks and online resources.
Here are some additional things to keep in mind when using the t table:
- The t table is only valid for the t distribution. Other distributions, such as the normal distribution, have different critical values.
- The t table is only accurate for large samples. For small pieces, you should use the Studentized range table instead.
- The t table is one of many ways to find the critical value of t. You can also use a statistical calculator or software program.
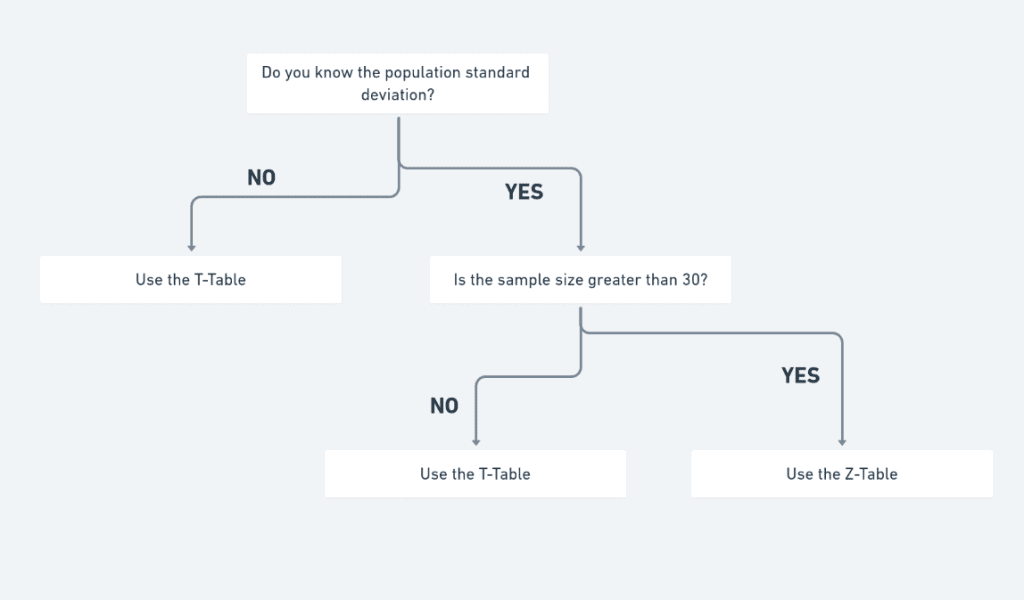
How to Use the T-Table
Here are the steps on how to use the t-table:
- Choose the type of t-test you are conducting. There are two types of t-tests: one-tailed and two-tailed.
-
- A one-tailed t-test is used when you only have a directional hypothesis. For example, you might hypothesize that population A’s mean is more significant than population B’s.
- A two-tailed t-test is used when you have a non-directional hypothesis. For example, you might hypothesize that the means of two populations are different.
- Calculate the degrees of freedom. The degrees of freedom are the number of independent observations in your sample.
- Choose a significance level. The importance level is the possibility of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true. The most typical matter levels are 0.05 and 0.01.
- Find the critical value of t in the t table. The t table is usually organized by degrees of freedom and significance level.
Here is an example of how to use the t-table. Suppose you are conducting a one-tailed t-test with 10 degrees of independence and an effectiveness level of 0.05. The critical value of t for this test is 1.812. This means that if the t statistic for your test is more significant than 1.812, you can leave the null hypothesis at the 0.05 importance level.
Here are some additional things to keep in mind when using the t-table:
- The t table is only valid for the t distribution. Other distributions, such as the normal distribution, have different critical values.
- The t table is only accurate for large samples. For small pieces, you should use the Studentized range table instead.
- The t table is one of many ways to find the critical value of t. You can also use a statistical calculator or software program.
The t-distribution is used when the people’s expected variation is unknown, and the sample size is small. This is because the t-distribution is more spread out than the normal distribution, making its estimates more conservative.
The t-distribution is used in a variety of statistical tests, including:
- T-tests: T-tests are used to approximate the means of two sets. The most common t-test is the t-test for independent samples, used when the two groups are separate. The t-test for paired samples is used when the two groups are paired, such as when the same participants are measured twice.
- Confidence intervals: Confidence intervals estimate the population mean or other population parameter. The t-distribution is used to construct confidence intervals when the population standard deviation is unknown.
- Hypothesis testing: Hypothesis testing determines whether there is enough evidence to support a claim about the population. The t-distribution is used for hypothesis tests when the population standard deviation is unknown.
Here are some other situations where the t-distribution can be used:
- When the data is not normally distributed, the sample size is large enough.
- The sample size is small when the data is not normally distributed and the population standard deviation is known.
- When the data is not normally distributed, the sampling size is small, and the people’s expected deviation is anonymous.
The t-distribution should be used whenever the population standard deviation is unknown, and the sample size is small. However, it can also be used in other situations, such as when the data is not normally distributed.
T Table vs Z Table vs Chi-Square Table
Here is a table summarizing the key differences between the t table, z table, and chi-square table:
| Feature | t table | z table | chi-square table |
|---|---|---|---|
| Distribution | t distribution | Standard normal distribution | Chi-square distribution |
| Used for | t-tests | z-tests | Chi-square tests |
| Population standard deviation | Unknown | Known | Unknown |
| Sample size | Small | Large | Large or small |